After more than 20 years using experience, most shipyard are very familiar with the NEW technologies of marine launching airbags, which can also used as salvage airbag and water-blocking airbags, but there still are some end-users being not confident with it. So, Qingdao Evergreen summarize below advantages of these airbags to address customers’ concern:
1. Significant Cost Savings
• Low procurement and operational costs: Compared to constructing dry docks or purchasing large-scale lifting equipment, the purchase cost of airbags is considerably lower. Moreover, they eliminate the need for maintaining complex facilities over the long term, reducing capital investment by 30%-50%.
• Easy maintenance: Only regular inspections of the airbag’s exterior, valves, and other components are required, eliminating the need for specialized maintenance equipment and drastically reducing labor and time costs.
2. High Operational Flexibility and Stability
• Controllable buoyancy: By adjusting the air pressure inside the airbags, the buoyancy can be precisely controlled to support the ship’s weight, avoiding imbalances caused by uneven friction in traditional slipway launches (e.g., the detachment of skids leading to ship tilting, as seen in the North Korean destroyer incident).
• Flexible attitude adjustment: The ship’s tilt angle can be controlled by gradually deflating or inflating the airbags, ensuring a smoother launching process. For instance, the “aft tilting” technique mentioned in the references leverages gravity for a natural water entry, minimizing mechanical intervention risks.
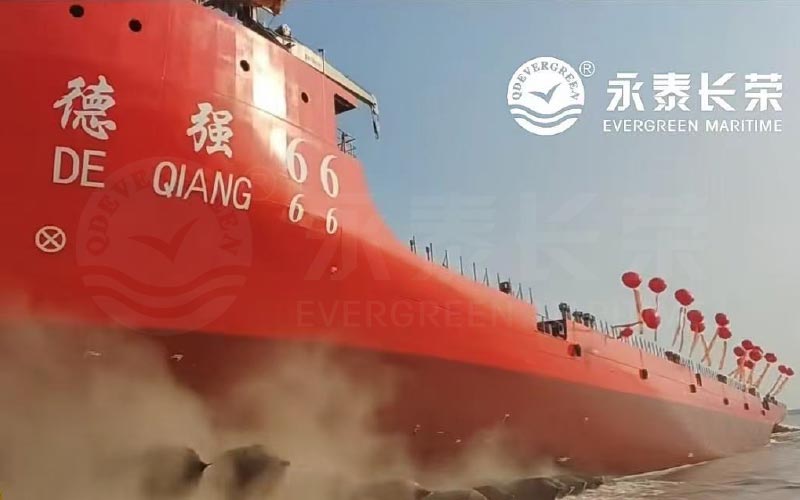

3. Substantial Reduction in Safety Risks
• Avoidance of traditional accident risks: Traditional slipway launches are prone to accidents due to parallelism deviations in skids (e.g., the stern skid detaching first in the North Korean incident, causing hull damage) or sudden changes in friction coefficients. Airbags distribute risks evenly through uniform pressure bearing.
• Strong resistance to environmental disturbances: Airbags adapt well to changes in tides, wind, and other external factors, reducing the impact of sudden forces on the hull.
4. Outstanding Applicability and Convenience
• Easy transportation and storage: When deflated, airbags are compact and lightweight, enabling rapid transportation to different sites—ideal for temporary construction or remote shipyards.
• Versatile application: Suitable for ships of various tonnages (from small fishing boats to 5,000-ton destroyers) and complex terrains (e.g., inclined shorelines).
5. Improved Construction Efficiency
• Quick deployment: No need for prolonged construction of slipways or dry docks; airbags can be deployed within hours, shortening project timelines. For example, repairing the damaged hull in the North Korean incident took about two weeks, whereas airbag deployment would take only a few hours.
• Reusability: Airbags have a long lifespan (high-quality products can be reused over 50 times), making them suitable for multiple ship launches.
Case Comparison: Traditional Slipway vs. Airbag Launching
• North Korean Destroyer Incident (Traditional Slipway): Skid detachment caused hull imbalance and damage, requiring approximately two weeks for repairs.
• Airbag Solution: If airbags had been used, real-time attitude adjustments via pressure control could have prevented structural damage, reducing repair time to 2-3 days.
Summary
Marine launching airbags are the preferred choice for modern ship launches due to their low cost, high safety, and strong adaptability, suitable for all-sized shipyards or emergency repair scenarios. Their technical principles share similarities with water-blocking airbags for drainage pipes (e.g., the sealing performance and specification adaptability demonstrated in the Dalian case), both reflecting the flexible application of inflatable tools in engineering fields.
